Introduction to Essential Chemistry Instruments
In chemistry, the right tools are crucial for conducting experiments, making accurate measurements, and obtaining reliable results. Whether in an academic setting, research lab, or industrial context, chemistry instruments play a key role in understanding chemical reactions, analyzing substances, and developing new compounds. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the main types of chemistry instruments, classified into essential categories for ease of understanding.
1. Basic Measurement Instruments
Precise measurement is foundational in chemistry, ensuring accuracy in data and repeatability in experiments. These instruments include:
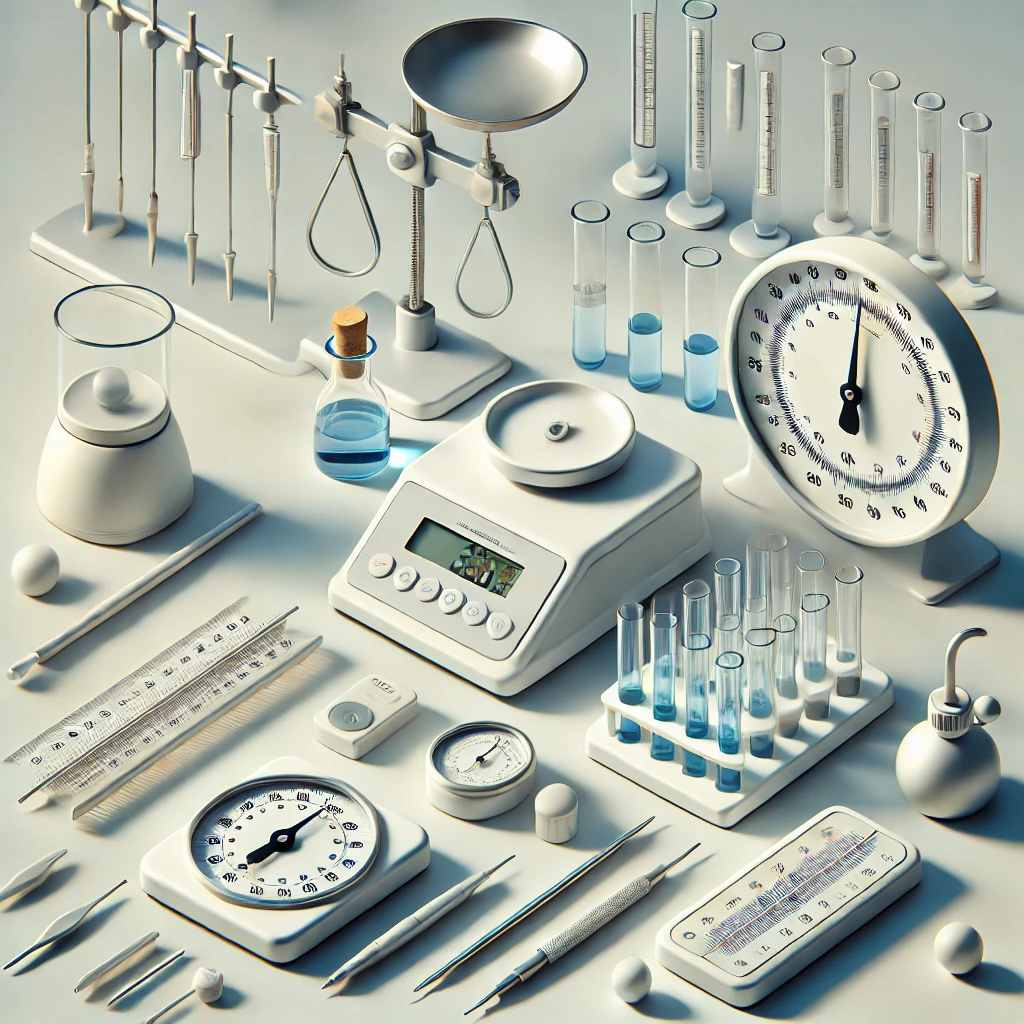

- Balances and Scales
Used to measure mass with high precision, ranging from digital analytical balances with milligram precision to larger scales for bulk materials. - Thermometers
Critical for monitoring reaction temperatures, from traditional mercury thermometers to digital probes with greater accuracy. - Pipettes and Burettes
For measuring and transferring precise liquid volumes. Pipettes (single and multi-channel) and burettes (used in titration) are essential for quantitative analysis.
2. Laboratory Glassware
Glassware is central to conducting reactions and handling chemicals safely. Some primary types include:
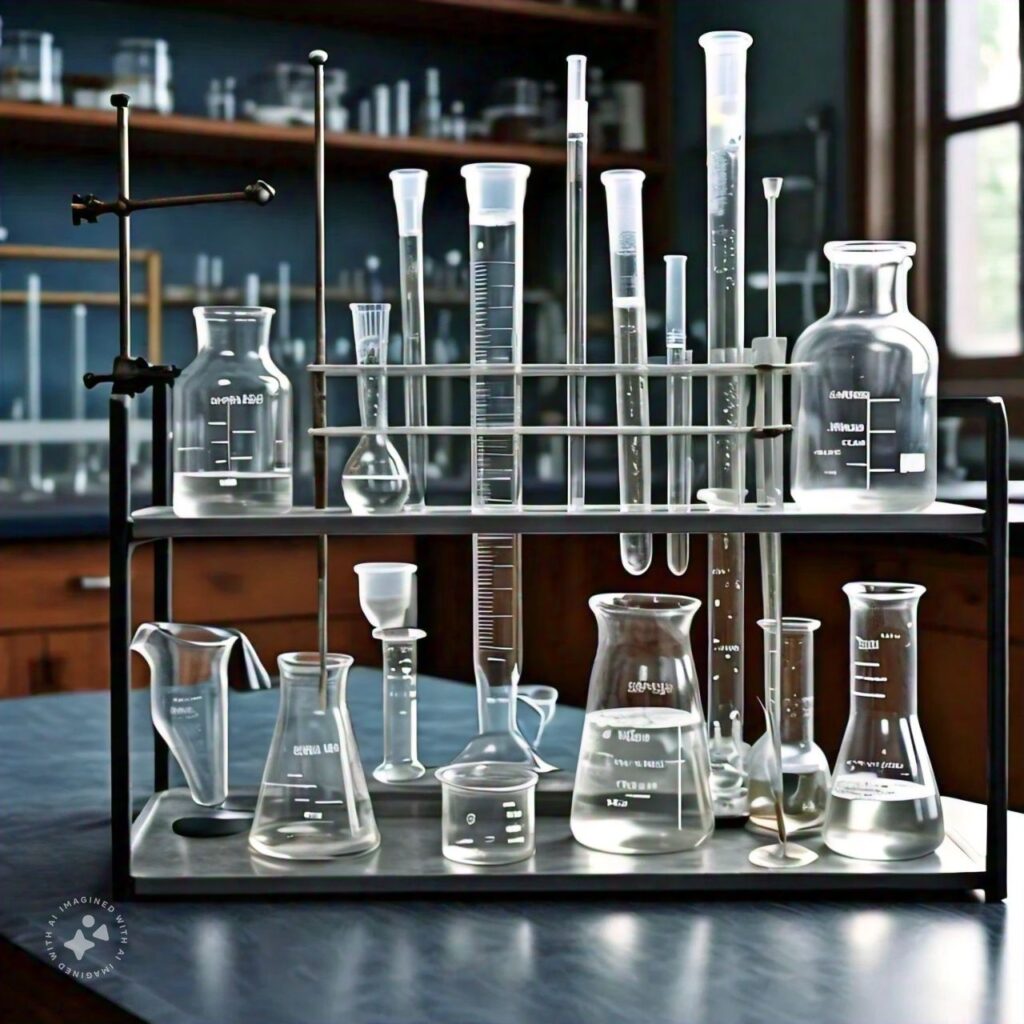

- Beakers and Flasks
Beakers are versatile containers for mixing and heating, while Erlenmeyer and volumetric flasks provide precision in preparing solutions. - Graduated Cylinders
Used for accurate liquid measurements, with graduated markings for easy volume identification. - Test Tubes
Widely used for holding small samples or conducting miniaturized reactions. - Separatory Funnels
For liquid-liquid extraction, allowing separation of immiscible liquids by density.
3. Heating and Cooling Equipment
Many chemical reactions require specific temperatures to proceed. Key heating and cooling instruments include:
- Bunsen Burners and Hot Plates
Bunsen burners provide a flame source, while hot plates allow for controlled, even heating, often with magnetic stirrers. - Water Baths
Used to heat samples uniformly in a controlled environment, suitable for reactions needing moderate heat. - Refrigerators and Freezers
Essential for storing temperature-sensitive chemicals and samples at low temperatures.

4. Mixing and Stirring Instruments
Homogenizing mixtures or ensuring complete solubility of reactants requires reliable mixing tools, such as:

- Magnetic Stirrers
Frequently used with hot plates, these devices use a rotating magnet to mix solutions consistently. - Shakers and Vortex Mixers
Shakers (orbital, linear) and vortex mixers provide agitation for samples, commonly used in biological and chemical labs.
5. Filtration and Separation Tools
Separating mixtures into their individual components is a vital part of chemical analysis. Key tools include:
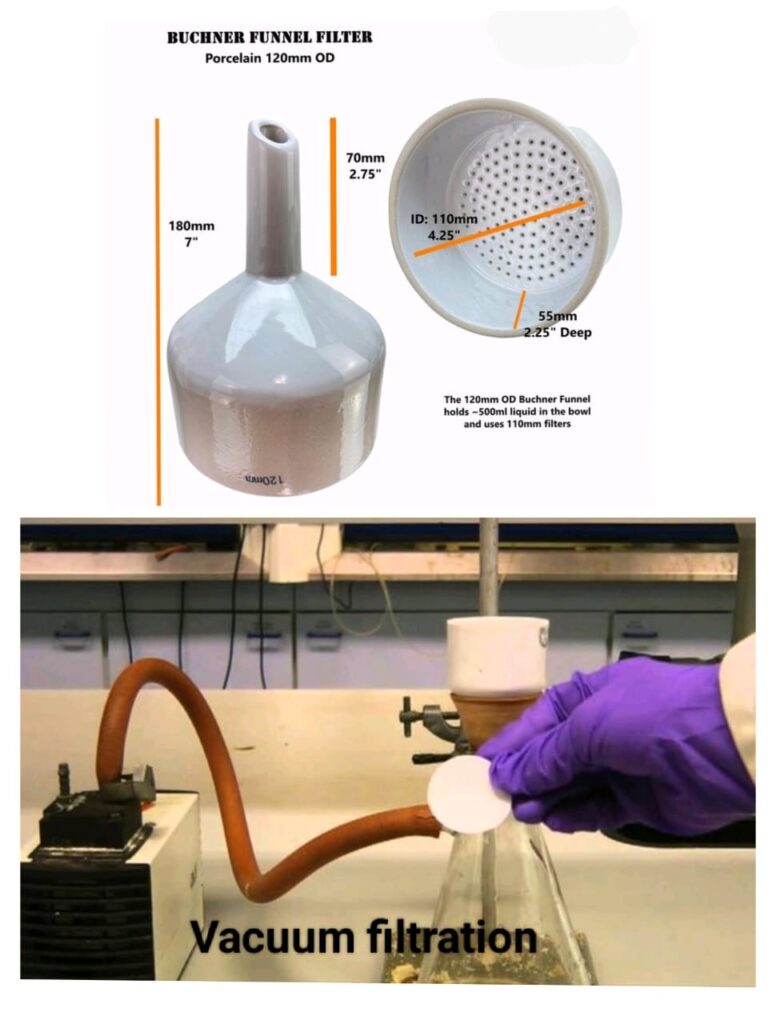
- Filters and Filtration Apparatus
From simple filter papers to complex Buchner funnels and vacuum filtration setups, these are essential for isolating solids from liquids.
centrifuge machine: A centrifuge is a laboratory device that separates components in a liquid based on density by spinning samples at high speeds. This creates centrifugal force, causing heavier particles to move outward, while lighter components remain closer to the center. Centrifuges are essential for separating blood, chemicals, and other mixtures in lab settings.

6. Analytical Instruments
Analyzing chemical properties and concentrations accurately relies on sophisticated equipment:
- Spectrophotometers
These devices measure light absorbance at various wavelengths, enabling quantification of substances in a solution. - pH Meters
Essential for determining acidity or alkalinity, with digital meters providing accurate pH readings. - Chromatography Systems
Gas Chromatography (GC) and Liquid Chromatography (LC) systems are used for separating complex mixtures, essential in drug testing and environmental analysis.

7. Safety Equipment
Ensuring safety in a chemistry lab is non-negotiable. Key safety tools include:
- Fume Hoods
Protects users from hazardous fumes by venting out toxic gases, essential for handling volatile substances. - Eyewash Stations and Emergency Showers
Located in labs for quick decontamination in case of accidental spills or exposure. - Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Includes lab coats, gloves, goggles, and sometimes face shields, protecting against splashes, burns, and exposure.
8. Specialized Equipment
Certain experiments require unique instruments for specialized analysis or preparation:
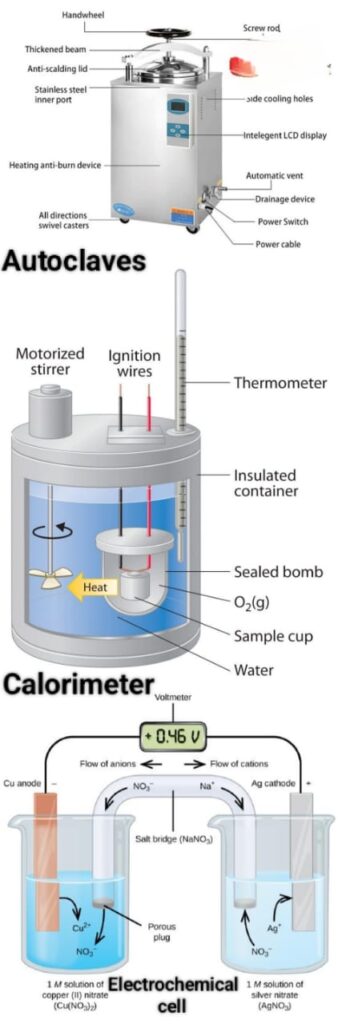
- Autoclaves
For sterilizing lab equipment, primarily used in microbiology and medical research settings. - Calorimeters
Measure the heat change in reactions, useful in thermochemistry and metabolic studies. - Electrochemical Cells
Essential for studies involving electrochemistry, such as in battery research.
Conclusion
This comprehensive overview highlights the essential categories and tools in chemistry labs, from basic measurement to sophisticated analysis instruments. With this knowledge, researchers can select the appropriate tools to enhance safety, precision, and effectiveness in their experiments, paving the way for scientific discovery and innovation.

CHEMISTRY INSTRUMENTS
Chemistry tools are essential for precise experiments, enabling scientific discovery.
exactly